A native deciduous tree species in Ireland, commonly found in woodlands, hedgerows, and parklands.
Recognising the Wild Cherry Tree:
-
Leaves: The leaves of the Wild Cherry tree are alternate, oval-shaped, and finely toothed along the margins. They are dark green in colour and turn yellow to orange-red in autumn before falling.
-
Bark: The bark of the Wild Cherry tree is smooth and reddish-brown when young, becoming rougher and darker with age. It often develops horizontal lenticels (raised pores in the stem of a woody plant that allows gas exchange between the atmosphere and the internal tissues) and vertical cracks.
-
Flowers: Wild Cherry trees produce clusters of small, white flowers in early to mid-spring. The flowers have five petals and appear before or alongside the emergence of the leaves.
-
Fruit: After flowering, Wild Cherry trees produce small, red to black fruits known as cherries. These cherries are edible for humans and are often harvested for culinary use.
-
Habitat: Wild Cherry trees are commonly found in a variety of habitats, including woodlands, hedgerows, and parklands. They prefer well-drained soils and are often associated with other broadleaf tree species.
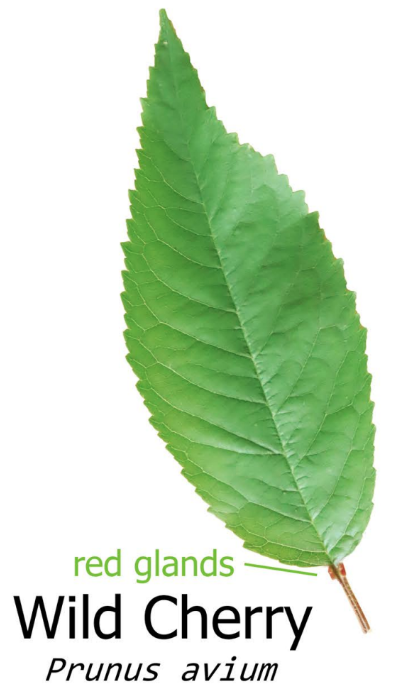


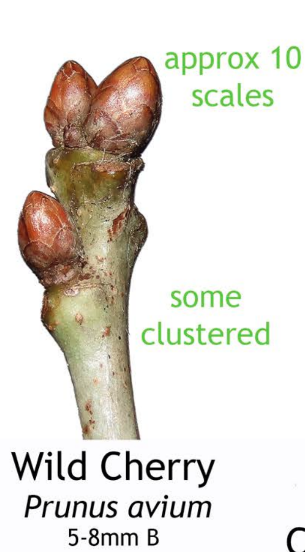
5 Interesting Facts about the Wild Cherry Tree:
-
Edible Fruit: The cherries produced by Wild Cherry trees are edible for humans and are often used in culinary applications such as jams, jellies, pies, and beverages. They have a sweet flavour when ripe and can be enjoyed fresh or processed.
-
Cultural Significance: In folklore and traditional medicine, Wild Cherry trees have been associated with various superstitions and beliefs. In some cultures, the tree was thought to symbolise fertility, while in others, it was believed to have medicinal properties.
-
Wildlife Habitat: Wild Cherry trees provide habitat and food for a variety of wildlife species. Birds feed on the fruits (cherries), while insects pollinate the flowers and feed on the foliage. Mammals such as deer may also browse on the foliage.
-
Woodcraft: The wood of Wild Cherry trees is valued for its hardness, durability, and attractive grain pattern. It is used in a variety of woodworking applications such as furniture making, cabinetry, flooring, and musical instruments.
-
Early Flowering: Wild Cherry trees are among the first tree species to flower in spring, often before or alongside the emergence of the leaves. The fragrant flowers attract pollinators such as bees, butterflies, and moths, contributing to early-season nectar sources.
Uses of the Wild Cherry Tree:
-
Edible Fruit: The cherries produced by Wild Cherry trees are harvested for culinary use. They can be eaten fresh, cooked into preserves, or used as flavourings for various dishes and beverages. Cherry products such as jams, jellies, pies, and liqueurs are popular culinary creations.
-
Woodcraft: The wood of Wild Cherry trees is highly valued for its aesthetic qualities and workability. It is used in fine woodworking projects such as furniture making, cabinetry, turned objects, and musical instruments. The wood has a warm, reddish-brown colour and a smooth, satiny texture.
-
Wildlife Habitat: Wild Cherry trees contribute to biodiversity by providing habitat and food for a variety of wildlife species. Their presence enhances habitat complexity and provides food, shelter, and nesting sites for birds, insects, and mammals, contributing to overall biodiversity in woodland and parkland ecosystems.
Contribution to Biodiversity:
-
Habitat Provider: Wild Cherry trees create diverse micro-habitats that support a wide range of plant and animal species. Their presence enhances habitat complexity and provides food, shelter, and nesting sites for wildlife, contributing to overall biodiversity in woodland and parkland ecosystems.
-
Pollinator Support: The fragrant flowers of Wild Cherry trees provide an important nectar and pollen source for early-emerging pollinators such as bees, butterflies, and moths. This supports pollinator populations and contributes to the health of ecosystems.
-
Seed Dispersal: Birds that feed on the fruits (cherries) of Wild Cherry trees help disperse the seeds over a wide area through their droppings. This promotes the regeneration and spread of Wild Cherry trees in natural habitats, contributing to the diversity and resilience of woodland and parkland ecosystems.
In summary, the Wild Cherry tree is recognisable by its fragrant flowers, edible fruits, and toothed leaves. It holds cultural significance, provides valuable resources for wildlife, and contributes to biodiversity and ecosystem health in Ireland's woodlands and parklands. Additionally, it serves as an important food source for birds and other wildlife, supports pollinator populations, and enhances habitat complexity in natural ecosystems.
Images taken from the beautiful posters created by Phil Barnett and you can download these and/or purchase other great designs from his online shop.
