A native deciduous tree species in Ireland, commonly found in woodlands, hedgerows, and upland areas.
Recognising the Rowan Tree:
-
Leaves: The leaves of the Rowan tree are alternate, pinnately compound, and have serrated margins. Each leaf typically consists of several pairs of leaflets and a terminal leaflet. The leaflets are dark green in colour and turn yellow to orange-red in autumn before falling.
-
Bark: The bark of the Rowan tree is smooth and greyish-brown when young, becoming rougher and darker with age. It often develops shallow fissures and irregular ridges.
-
Flowers: Rowan trees produce clusters of small, creamy-white flowers in late spring to early summer. The flowers have five petals and are arranged in large, flat-topped clusters known as corymbs.
-
Berries: After flowering, Rowan trees produce clusters of small, round berries known as rowan berries or mountain ash berries. The berries ripen from green to bright red or orange in late summer to early autumn and are a key characteristic of the tree.
-
Habitat: Rowan trees are commonly found in a variety of habitats, including woodlands, hedgerows, upland areas, and mixed-species stands. They prefer moist, well-drained soils and are often associated with other broadleaf tree species.


5 Interesting Facts about the Rowan Tree:
-
Cultural Significance: Rowan trees have long been associated with folklore, mythology, and superstition. In Celtic and other European traditions, Rowan trees were believed to have protective properties and were often planted near homes to ward off evil spirits and bring good luck.
-
Wildlife Food Source: Rowan berries are an important food source for birds, particularly thrushes, blackbirds, and waxwings. The berries are rich in vitamins and antioxidants and provide valuable energy for migrating birds and wintering populations.
-
Traditional Uses: Various parts of the Rowan tree have been used in traditional crafts, cuisine, and medicine. The wood is valued for its fine grain and has been used for making tools, furniture, and musical instruments. The berries are used to make jams, jellies, syrups, and alcoholic beverages, while the bark and leaves have been used in herbal medicine.
-
Ecological Succession: Rowan trees are pioneer species that colonise disturbed or degraded habitats and facilitate ecological succession. They have the ability to grow in a wide range of soil conditions and climates, making them important for reforestation and habitat restoration efforts.
-
Attractive to Pollinators: The flowers of Rowan trees are attractive to a variety of pollinators, including bees, butterflies, and moths. They provide nectar and pollen for pollinators in spring and early summer, supporting pollinator populations and contributing to the health of ecosystems.
Uses of the Rowan Tree:
-
Wildlife Habitat: Rowan trees provide valuable habitat and food for a variety of wildlife species. Their berries are an important food source for birds, while the foliage provides shelter and nesting sites for birds and small mammals.
-
Traditional Medicine: Various parts of the Rowan tree, including the berries, bark, and leaves, have been used in traditional herbal medicine. Rowan berries are high in vitamin C and antioxidants and have been used to make remedies for colds, flu, and other ailments.
-
Ornamental Planting: Rowan trees are valued in landscaping for their ornamental qualities, including attractive foliage, flowers, and berries. They are often planted in parks, gardens, and landscapes as specimen trees, shade trees, and focal points.
Contribution to Biodiversity:
-
Wildlife Food Source: Rowan trees contribute to biodiversity by providing habitat and food for a variety of wildlife species. Their berries are an important food source for birds, particularly during the autumn and winter months when other food may be scarce. This supports bird populations and helps maintain ecosystem balance.
-
Pollinator Support: The flowers of Rowan trees provide nectar and pollen for a variety of pollinators, including bees, butterflies, and moths. This supports pollinator populations and contributes to the health of ecosystems by promoting plant reproduction and diversity.
-
Seed Dispersal: Rowan trees play a role in seed dispersal by producing berries that are eaten by birds and other animals. The seeds are then dispersed through the animals' droppings, helping to colonise new areas and establish diverse plant communities.
In summary, the Rowan tree is recognisable by its pinnately compound leaves, clusters of white flowers, and bright red or orange berries. It holds cultural significance, provides valuable resources for wildlife, and contributes to biodiversity and ecosystem health in Ireland's woodlands, hedgerows, and upland areas. Additionally, it serves as a food source for birds, supports pollinator populations, and enhances habitat complexity in natural ecosystems.
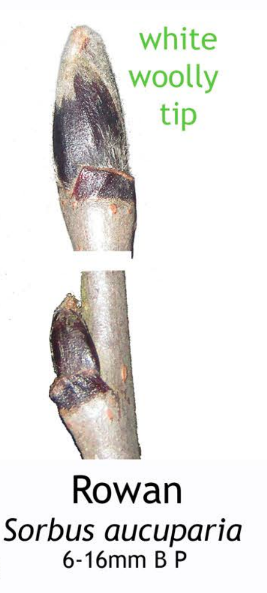
Images taken from the beautiful posters created by Phil Barnett and you can download these and/or purchase other great designs from his online shop.
