A native deciduous tree species in Ireland, commonly found in woodlands, forests, and parklands.
Recognising the Pendunculate Oak Tree:
-
Leaves: The leaves of the Pendunculate Oak tree are alternate, lobed, and have deep sinuses between the lobes. They are dark green in colour and turn golden-yellow to brown in autumn before falling.
-
Bark: The bark of the Pendunculate Oak tree is greyish-brown and develops shallow fissures and ridges with age. It has a rough texture and becomes more textured over time.
-
Acorns: Pendunculate Oak trees produce large acorns that are borne on long stalks (peduncles). The acorns have distinctive cupules with overlapping scales.
-
Shape: Pendunculate Oak trees have a broad, spreading canopy with sturdy branches and a straight, tall trunk. They can grow to significant heights and are often characterised by their imposing presence in the landscape.
-
Habitat: Pendunculate Oak trees are commonly found in a variety of habitats, including woodlands, forests, parklands, and hedgerows. They prefer moist, well-drained soils and are often associated with other broadleaf tree species.


5 Interesting Facts about the Pendunculate Oak Tree:
-
Longevity: Pendunculate Oak trees are known for their longevity, with some specimens living for several hundred years. They are among the oldest living organisms in Ireland and have witnessed centuries of history and change.
-
Wildlife Habitat: Pendunculate Oak trees provide valuable habitat and food for a wide range of wildlife species. Birds such as jays, woodpeckers, and nuthatches feed on the acorns, while mammals such as squirrels, deer, and wild boar may also browse on the foliage and feed on the acorns.
-
Historical Significance: Pendunculate Oak trees have played a significant role in human history and culture. They have been revered as symbols of strength, endurance, and wisdom in folklore, mythology, and literature. Oak trees were also used historically for shipbuilding, timber construction, and as a source of tannin for leather production.
-
Ecosystem Services: Pendunculate Oak trees provide a wide range of ecosystem services, including carbon sequestration, air and water purification, soil stabilisation, and biodiversity support. Their presence enhances habitat complexity and provides food, shelter, and nesting sites for wildlife, contributing to overall ecosystem health and resilience.
-
Regeneration: Pendunculate Oak trees have the ability to regenerate naturally through the dispersal of acorns and the growth of new seedlings. They also have the capacity to coppice and regenerate from stump sprouts, which has been utilised in traditional woodland management practices.
Uses of the Pendunculate Oak Tree:
-
Timber: Pendunculate Oak wood is highly valued for its strength, durability, and attractive grain pattern. It is used in a wide range of applications, including furniture making, flooring, joinery, cabinetry, cooperage (barrel making), and construction.
-
Wildlife Habitat: Pendunculate Oak trees provide valuable habitat and food for a variety of wildlife species. Their presence enhances habitat complexity and supports biodiversity in woodlands, forests, and parklands.
-
Cultural and Recreational Use: Pendunculate Oak trees are valued for their aesthetic and cultural significance. They are often planted in parks, gardens, and landscapes as specimen trees, shade trees, and focal points. They also provide recreational opportunities for activities such as hiking, picnicking, and wildlife watching.
Contribution to Biodiversity:
-
Habitat Provider: Pendunculate Oak trees contribute to biodiversity by providing habitat and food for a wide range of wildlife species. Their presence enhances habitat complexity and supports populations of birds, mammals, insects, and other organisms in woodlands, forests, and parklands.
-
Nutrient Cycling: Pendunculate Oak trees play a role in nutrient cycling by absorbing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and releasing oxygen through photosynthesis. They also cycle nutrients through their leaves, branches, and roots, contributing to soil fertility and ecosystem productivity.
-
Soil Health: Pendunculate Oak trees help maintain soil health and stability through their extensive root systems, which prevent erosion, improve soil structure, and promote water infiltration and retention. Their presence contributes to the overall health and resilience of woodland and forest ecosystems.
In summary, the Pendunculate Oak tree is recognisable by its lobed leaves, large acorns, and imposing stature. It holds cultural significance, provides valuable resources for wildlife, and contributes to biodiversity and ecosystem health in Ireland's woodlands, forests, and parklands. Additionally, it serves as a source of timber, supports recreational activities, and enhances habitat complexity in natural ecosystems.
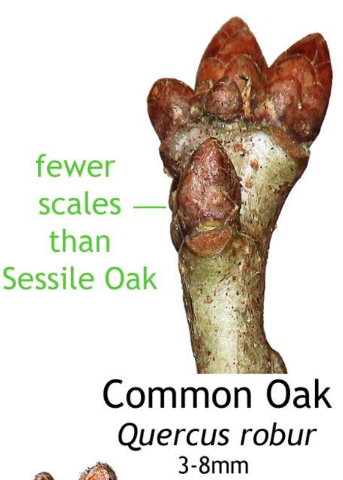
Images taken from the beautiful posters created by Phil Barnett and you can download these and/or purchase other great designs from his online shop.
