A native tree species in Ireland, commonly found in a variety of habitats such as woodlands, heathlands, and wetlands.
Recognising the Downy Birch:
-
Leaves: The leaves of the Downy Birch are alternate, simple, and triangular-ovate in shape, with serrated margins. They are typically dark green on top and paler underneath, with a downy or hairy texture on the underside.
-
Bark: The bark of the Downy Birch is smooth and pale gray or white when young, becoming darker and more fissured with age. It often develops black triangular markings, particularly near the base of the trunk.
-
Catkins: Downy Birch trees produce male and female catkins on separate trees. Male catkins are long and yellow-brown, while female catkins are shorter and greenish.
-
Habitat: Downy Birch trees are commonly found in moist, acidic soils in woodlands, heathlands, and peat bogs. They are often associated with other wetland species and are tolerant of waterlogged conditions.
-
Size: Downy Birch trees are typically medium-sized, reaching heights of 15-25 meters, with a slender trunk and a narrow, conical crown.


5 Interesting Facts about the Downy Birch:
-
Tolerance to Wet Conditions: Downy Birch trees are highly adapted to waterlogged soils and are commonly found in wetland habitats such as bogs and fens. Their ability to thrive in these conditions makes them important components of wetland ecosystems.
-
Wildlife Habitat: Downy Birch trees provide habitat and food for a variety of wildlife species. Birds nest in their branches, while insects feed on their leaves and sap. Mammals such as deer may also browse on the foliage.
-
Traditional Uses: The bark of Downy Birch trees has been used historically for various purposes. It can be stripped from the tree in thin sheets and used for roofing, basket weaving, and other crafts. The inner bark has also been used as a traditional remedy for various ailments.
-
Pioneer Species: Downy Birch trees are often among the first tree species to colonize disturbed or barren landscapes, such as areas affected by wildfires or clear-cutting. Their rapid growth and ability to fix nitrogen in the soil help prepare the ground for the establishment of other plant species.
-
Allelopathic Properties: Downy Birch trees release chemicals into the soil through their roots and leaf litter, which can inhibit the growth of competing plant species. This allelopathic effect helps Downy Birch trees maintain dominance in their habitat.
Uses of the Downy Birch Tree:
-
Wood Products: Downy Birch wood is relatively soft and lightweight, making it suitable for a variety of products such as plywood, veneer, and pulpwood for paper production. It is also used for making tool handles, furniture components, and fuel wood.
-
Landscaping: Downy Birch trees are planted for ornamental purposes in parks, gardens, and landscapes, particularly for their attractive bark, foliage, and autumn color display. They are valued for their ability to tolerate a wide range of soil conditions and their wildlife-friendly attributes.
-
Ecological Restoration: Downy Birch trees are valuable for reforestation and ecological restoration projects, particularly in wetland habitats. Their ability to colonize disturbed areas and improve soil conditions helps restore biodiversity and ecosystem function to degraded landscapes.
Contribution to Biodiversity:
-
Habitat Provider: Downy Birch trees create diverse micro-habitats that support a wide range of plant and animal species. Their presence enhances habitat complexity and provides food, shelter, and nesting sites for wildlife, contributing to overall biodiversity in forest ecosystems.
-
Soil Improvement: Downy Birch trees have the ability to fix nitrogen in the soil through symbiotic relationships with nitrogen-fixing bacteria in their root nodules. This helps enrich the soil and promote the growth of other plant species, further enhancing biodiversity in their habitat.
-
Erosion Control: Downy Birch trees help stabilise soils, prevent erosion, and reduce nutrient runoff in wetland habitats. Their extensive root systems and dense foliage provide effective ground cover, protecting fragile ecosystems from degradation and supporting a diverse array of plant and animal species.
In summary, the Downy Birch is recognisable by its triangular-ovate leaves, smooth white bark, and preference for wetland habitats. It holds ecological significance as a pioneer species, wildlife habitat provider, and contributor to biodiversity in Ireland's woodlands and wetlands. Additionally, it has practical uses in industries such as forestry, landscaping, and ecological restoration.
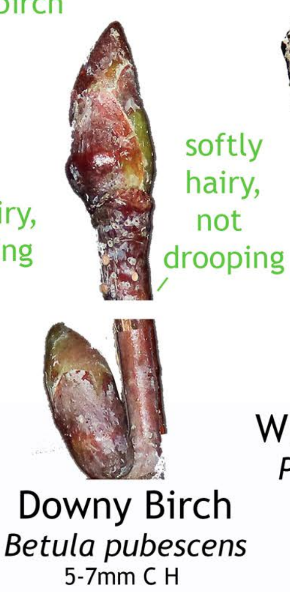
Images taken from the beautiful posters created by Phil Barnett and you can download these and/or purchase other great designs from his online shop.
