A native deciduous tree species in Ireland, typically found in woodlands, hedgerows, and moist habitats.
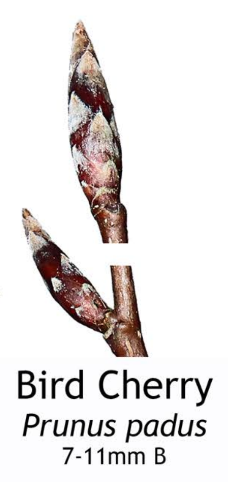
Recognising the Bird Cherry Tree:
-
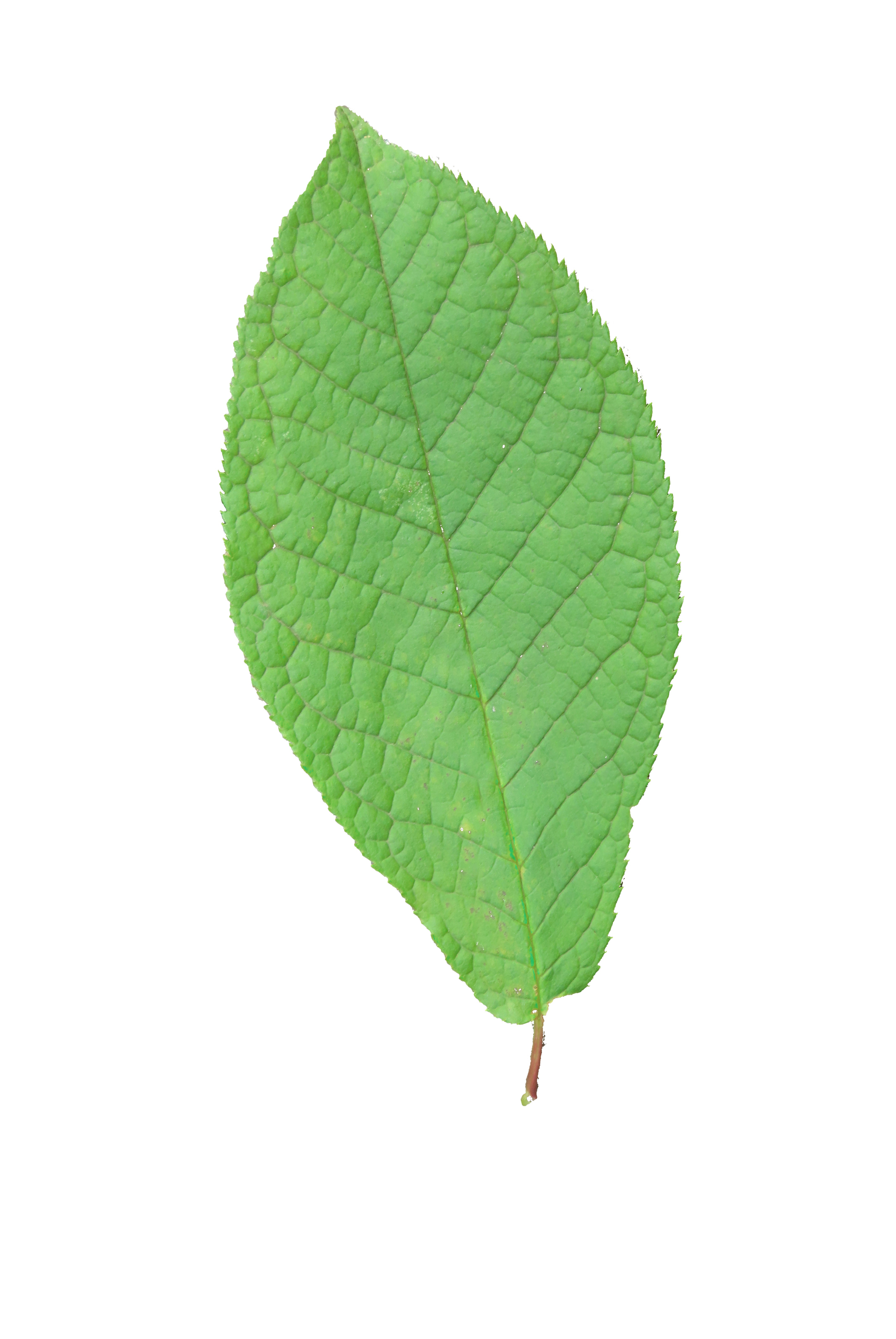
Leaves: The leaves of the Bird Cherry tree are alternate, oval-shaped, and finely toothed along the margins. They are dark green in color and turn yellow to orange in autumn before falling.
-
Bark: The bark of the Bird Cherry tree is smooth and greyish-brown when young, becoming rougher and darker with age. It often develops horizontal lenticels (raised pores in the stem of a woody plant that allows gas exchange between the atmosphere and the internal tissues).
-
Flowers: Bird Cherry trees produce clusters of small, white flowers in early to mid-spring. The flowers are highly fragrant and attract pollinators such as bees, butterflies, and moths.
-
Fruit: After flowering, Bird Cherry trees produce small, dark purple to black fruits known as cherries. These cherries are bitter and inedible for humans but are consumed by birds and other wildlife.
-
Habitat: Bird Cherry trees are commonly found in moist, well-drained soils in woodlands, hedgerows, and riparian areas. They are often associated with other wetland species and can tolerate a wide range of soil conditions.


5 Interesting Facts about the Bird Cherry Tree:
-
Wildlife Habitat: Bird Cherry trees provide habitat and food for a variety of wildlife species. Birds feed on the fruits (cherries), while insects pollinate the flowers and feed on the foliage. Mammals such as deer may also browse on the foliage.
-
Cultural Significance: In folklore and traditional medicine, Bird Cherry trees have been associated with various superstitions and beliefs. In some cultures, the tree was thought to ward off evil spirits, while in others, it was believed to have medicinal properties.
-
Nitrogen Fixation: Like other members of the Prunus genus, Bird Cherry trees have the ability to fix nitrogen in the soil through symbiotic relationships with nitrogen-fixing bacteria in their root nodules. This helps enrich the soil and promote the growth of other plant species.
-
Ornamental Value: Bird Cherry trees are planted for ornamental purposes in parks, gardens, and landscapes, particularly for their beautiful spring flowers and attractive autumn foliage. They are valued for their aesthetic appeal and ability to attract pollinators.
-
Biodiversity Support: Bird Cherry trees contribute to biodiversity by providing habitat and food for a variety of wildlife species. Their presence enhances habitat complexity and provides food, shelter, and nesting sites for birds, insects, and mammals, contributing to overall biodiversity in woodland and riparian ecosystems.
Uses of the Bird Cherry Tree:
-
Wildlife Food Source: The fruits (cherries) of Bird Cherry trees are an important food source for birds, particularly during the autumn and winter months when other food may be scarce. Birds such as thrushes, blackbirds, and waxwings feed on the cherries, helping to disperse the seeds and promote the regeneration of Bird Cherry trees.
-
Ornamental Planting: Bird Cherry trees are planted for ornamental purposes in parks, gardens, and landscapes, particularly for their beautiful spring flowers and attractive autumn foliage. They are valued for their aesthetic appeal and ability to attract pollinators.
-
Woodcraft: While not as commonly used as other tree species, the wood of Bird Cherry trees can be used for small woodworking projects such as carving, turning, and crafting. The wood is relatively hard and durable, with a fine grain and attractive colour.
Contribution to Biodiversity:
-
Habitat Provider: Bird Cherry trees create diverse micro-habitats that support a wide range of plant and animal species. Their presence enhances habitat complexity and provides food, shelter, and nesting sites for wildlife, contributing to overall biodiversity in woodland and riparian ecosystems.
-
Pollinator Support: The fragrant flowers of Bird Cherry trees provide an important nectar and pollen source for early-emerging pollinators such as bees, butterflies, and moths. This supports pollinator populations and contributes to the health of ecosystems.
-
Seed Dispersal: Birds that feed on the fruits (cherries) of Bird Cherry trees help disperse the seeds over a wide area through their droppings. This promotes the regeneration and spread of Bird Cherry trees in natural habitats, contributing to the diversity and resilience of woodland and riparian ecosystems.
In summary, the Bird Cherry tree is recognisable by its fragrant flowers, dark fruits (cherries), and toothed leaves. It holds cultural significance, provides valuable resources for wildlife, and contributes to biodiversity and ecosystem health in Ireland's woodlands and riparian areas. Additionally, it serves as an important food source for birds and other wildlife, supports pollinator populations, and enhances habitat complexity in natural ecosystems.
Images taken from the beautiful posters created by Phil Barnett and you can download these and/or purchase other great designs from his online shop.
