A native tree species in Ireland, particularly found in the southwest region.
Recognising the Arbutus Tree:
-
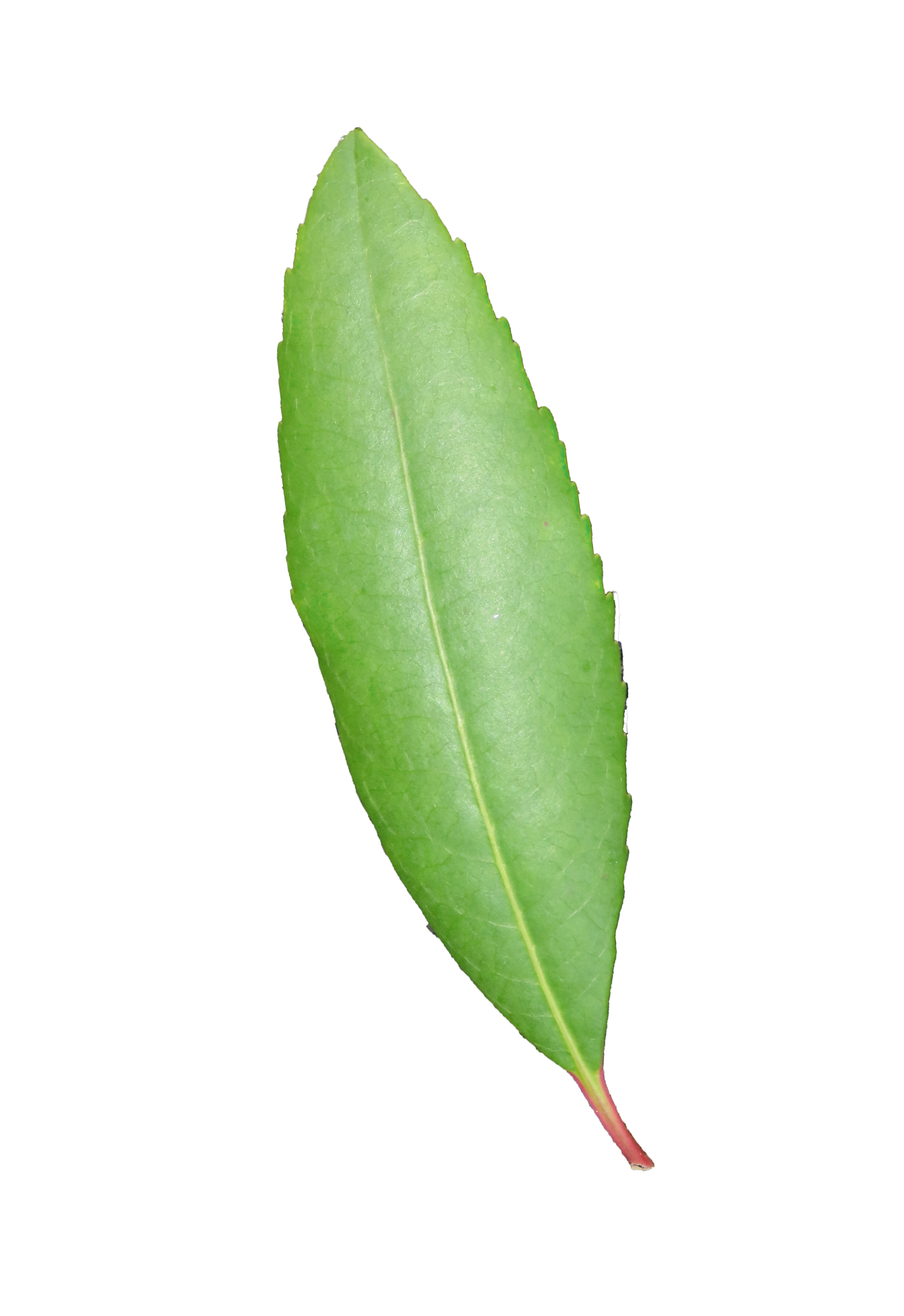
Leaves: The Arbutus tree has evergreen leaves that are dark green, glossy, and leathery in texture. They are oval-shaped with serrated edges.
-
Fruit: One of the most distinctive features of the Arbutus tree is its fruit. The fruits resemble small strawberries and are initially green, turning yellow-orange and finally red when ripe. It's not uncommon to find both flowers and ripe fruit on the tree at the same time.
-
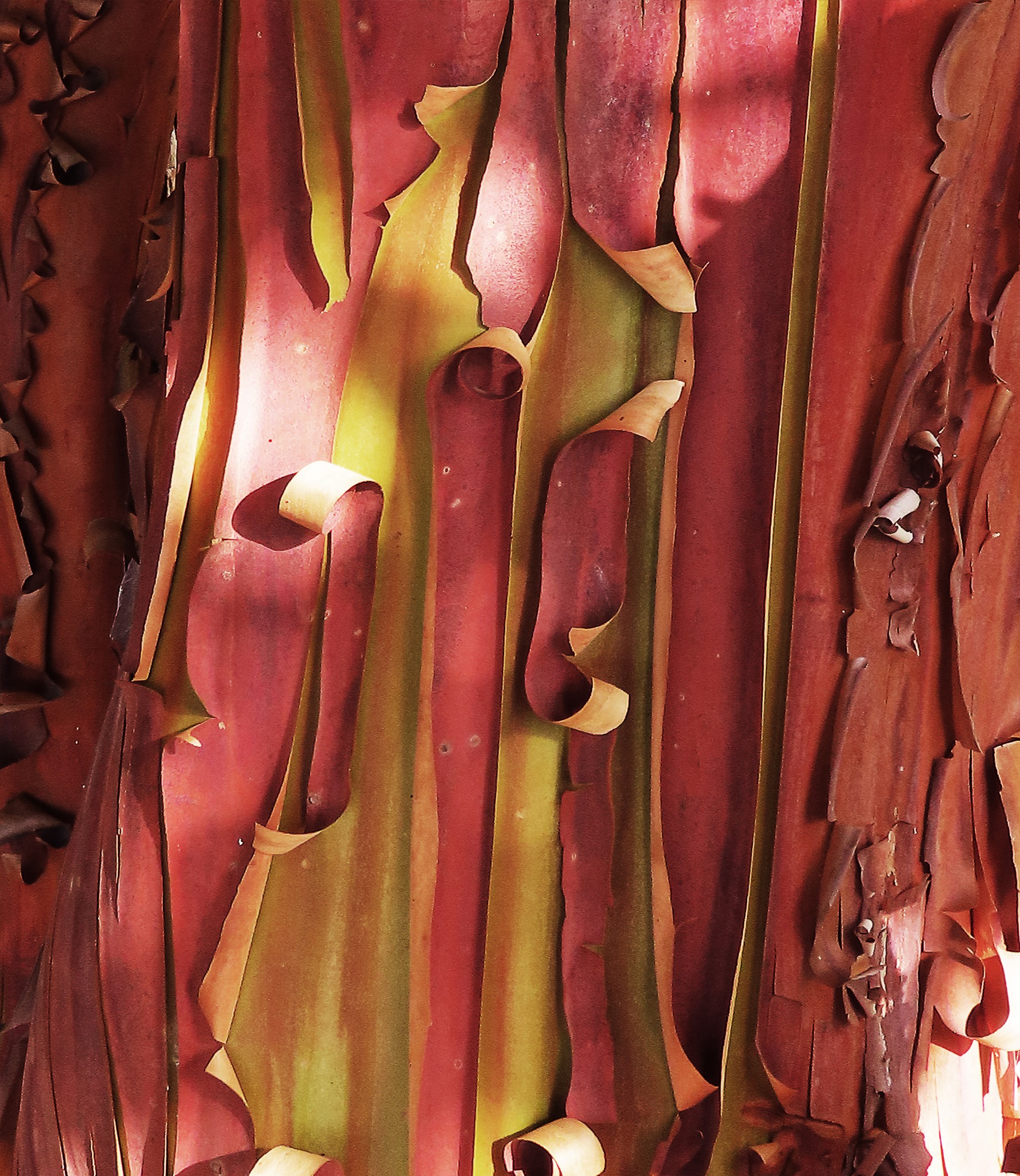
Bark: The bark of mature Arbutus trees is reddish-brown and peeling, revealing a smooth, reddish-orange inner bark.
-
Habitat: Arbutus trees are often found in rocky, acidic soils in coastal areas, heathlands, and woodlands, particularly in the southwest of Ireland.
-
Size: They typically grow as small to medium-sized trees, reaching heights of up to 10-15 meters.

5 Interesting Facts about the Arbutus Tree:
-
Symbolism: The Arbutus tree is associated with myths and legends, often symbolising resilience and endurance due to its ability to grow in harsh coastal environments.
-
Edible Fruit: While the fruit of the Arbutus tree, known as "Arbutus berries" or "strawberry tree fruit," is edible, it is not particularly tasty when raw due to its gritty texture and mild flavour. However, it can be used to make jams, jellies, and alcoholic beverages like liqueurs.
-
Evergreen Foliage: The Arbutus tree's evergreen leaves make it a valuable ornamental plant in gardens and landscapes, providing year-round greenery and texture.
-
Ecological Importance: Arbutus trees provide habitat and food for various wildlife species. Birds, such as thrushes and blackbirds, feed on the fruit, while the dense foliage offers shelter for small mammals and nesting sites for birds.
-
Medicinal Uses: Various parts of the Arbutus tree, including the leaves and bark, have been used in traditional medicine for their astringent, diuretic, and anti-inflammatory properties. However, caution should be exercised as some parts of the plant may be toxic in large quantities.
Uses of the Arbutus Tree:
-
Ornamental: Arbutus trees are commonly planted in gardens and parks for their attractive foliage, peeling bark, and ornamental fruit, adding year-round interest to landscapes.
-
Wood: While not widely used, Arbutus wood is occasionally harvested for small woodworking projects, such as crafting decorative items and turning bowls. Its fine grain and reddish colour can make it aesthetically pleasing for certain applications.
-
Cultural and Culinary: In addition to its ornamental and medicinal uses, the fruit of the Arbutus tree has culinary potential. While not as commonly utilised as other fruits, it can be made into jams, jellies, and beverages, adding a unique flavour to culinary creations.
Contribution to Biodiversity:
-
Wildlife Habitat: The Arbutus tree provides habitat and food for a variety of wildlife species, including birds, insects, and small mammals. Its fruit is an important food source for birds, particularly during the winter months when other food may be scarce.
-
Biodiversity Hotspot: Arbutus trees often grow in biodiverse ecosystems, such as coastal heathlands and woodlands, where they contribute to overall ecosystem health and resilience by supporting a diverse array of plant and animal species.
-
Soil Stabilisation: The deep root system of Arbutus trees helps stabilise soil, preventing erosion in coastal areas and contributing to the conservation of fragile coastal habitats.
In summary, the Arbutus tree is not only recognisable by its distinctive foliage, bark, and fruit but also holds cultural significance, provides various practical uses, and plays a vital role in supporting biodiversity in Ireland's coastal and woodland ecosystems.
Images taken from the beautiful posters created by Phil Barnett and you can download these and/or purchase other great designs from his online shop.
